Table of Content
- Expertise Expertise
- Services
- Blockchain
- Solutions
Exchange Development
Banking & Fintech
Wallet
Trading Bots
DEFI
NFT
Game Development
- Blog
- Company
- Get in Touch
March 28, 2025
Table of Content
Quick commerce, or Q-commerce, is redefining the landscape of on-demand retail by establishing a new benchmark for speed and convenience.
Unlike traditional e-commerce, which often involves delivery times ranging from days to weeks, Q-commerce focuses on delivering goods within minutes.
This shift is fueled by urban consumers' increasing demand for immediate access to everyday essentials, such as groceries and personal care items, making quick commerce a vital player in the modern retail ecosystem.
As we delve into this blog, we will explore the key characteristics that distinguish quick commerce from conventional e-commerce, its impact on consumer behavior, and how businesses adapt to meet the rising expectations for rapid delivery.
Let's get started!
Quick commerce, often referred to as Q-commerce, is a modern subset of e-commerce focused on delivering products at lightning speed, typically within 10 to 30 minutes.
It combines traditional online shopping with hyperlocal delivery networks and advanced logistics to cater to the immediate needs of urban consumers.
"Quick commerce redefines speed in online shopping, slashing delivery times to as little as 30 minutes thus far outpacing traditional e-commerce."
This model emphasizes convenience and speed, primarily targeting small orders of essentials like groceries, medicines, and personal care items.
By leveraging technologies such as AI-driven inventory management and dark stores , quick commerce ensures rapid delivery while reshaping consumer expectations in the digital retail space.
Quick commerce (Q-commerce) represents the latest evolution in the e-commerce landscape, building upon three distinct generations of e-commerce.
Each generation reflects advancements in technology, logistics, and consumer behavior, ultimately leading to the rise of Q-commerce which stands out from others by offering ultra-fast delivery to meet the growing demand for speed and convenience.
| 1st Generation E-Commerce: The Birth of Online Shopping | 2nd Generation E-Commerce: Social And Mobile Integration | 3rd Generation E-Commerce: Personalization And Instant Gratification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traits | Self-service platforms offering all products, primarily targeting households of 3–4 members. Delivery times were slow, often taking days. | The rise of mobile apps and social media marketing helped retailers engage consumers effectively. Delivery speeds improved slightly (2–3 days), with mega warehouses supporting logistics. | Advanced analytics enabled personalized shopping experiences. Consumers began demanding faster delivery (< hour), leading to localized fulfillment centers and two-wheeled delivery vehicles. |
| Key Example | Amazon's early years focused on selling books online, laying the foundation for digital retail but relying on traditional delivery methods. | Flipkart leveraged mobile commerce and mega warehouses to cater to growing online demand in India. | Amazon Prime introduced same-day delivery options globally, pushing the boundaries of speed in e-commerce. |
| Delivery Speed | Several days | 2–3 days | Less than an hour for select categories |
| Infrastructure | Superstores and privately owned cars for distribution | Delivery trucks and centralized warehouses | Local stores or warehouses close to urban areas |
| Focus | Discounts mattered most to consumers | Main products available with an emphasis on convenience | Speed mattered more than discounts |
Quick commerce emerged to address the growing demand for instant delivery, particularly in urban areas where convenience is paramount.
Unlike traditional e-commerce models, Q-commerce focuses on delivering essentials like groceries, personal care items, and medicines within minutes.Globally, this shift has been fueled by technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and hyper-localized services.
Operates in major cities across Europe and the US, delivering groceries within 10–15 minutes using dark stores close to urban centers. It focuses on essentials like fresh produce and household items.
Originating in Turkey and now operating in countries like the UK and the US, Getir delivers essentials such as snacks and groceries within 10 minutes using strategically located micro-warehouses.
A leader in quick commerce in the US, GoPuff delivers a wide range of products, from snacks to cleaning supplies, often within 30 minutes through centralized warehouses.
Initially focused on restaurant deliveries but expanded into grocery delivery with partnerships for rapid fulfillment within an hour.
Operating across Europe, the US, and Asia-Pacific regions, Wolt delivers food and essential products in under 30 minutes by partnering with local retailers.
Quick commerce operates through a streamlined, technology-driven process designed to deliver goods to consumers in a matter of minutes.
Here’s a breakdown of how it works,
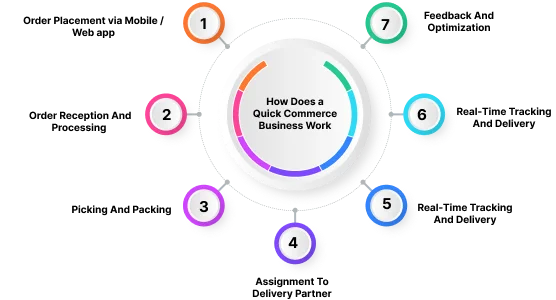
The process begins with the consumer placing an order through a dedicated mobile/ web application. These apps are designed for user-friendly navigation, allowing customers to easily browse products and add them to their cart.
Once the order is placed, it’s instantly received at the nearest "dark store" or micro-fulfillment center. These centers are strategically located in high-demand urban areas to minimize delivery distances.
Advanced inventory management systems ensure that the products displayed on the app are accurately stocked and available.
"Dark stores and micro-fulfillment centers are the backbone of Q-commerce, enabling instant delivery in urban areas."
Within the dark store, a team of pickers receives the order details and quickly gathers the items from the shelves. This process is optimized for speed, with pickers often using technology to locate items efficiently.
Items are then carefully packed to ensure they remain in good condition during transit.
Once the order is packed, it’s assigned to a delivery partner. Quick commerce companies often employ a network of independent contractors who use bikes, scooters, cars, or even walk to make deliveries.
Sophisticated algorithms determine the nearest available delivery partner to ensure minimal pickup time.
The delivery partner picks up the order and uses GPS navigation to find the customer’s location. Customers can track the delivery in real-time through the app, providing transparency and managing expectations.
Delivery partners are incentivized to complete deliveries quickly, often receiving bonuses for timely service.
The delivery partner hands the order to the customer, completing the transaction. Many quick commerce services offer contactless delivery options for added convenience and safety.
After the delivery is complete, customers have the option to provide feedback on their experience. This feedback is crucial for continuous improvement and optimization of the quick commerce process.
Data collected from orders, delivery times, and customer feedback is analyzed to refine processes, optimize inventory, and improve overall service quality!
Want to dive deeper into how Q-commerce businesses operate and make money?
Check out our in-depth guide on the Quick Commerce Business Model & Revenue Streams .
Unmatched Convenience
Customers experience unparalleled convenience with Q-commerce by eliminating the need to visit a physical store, stand in long queues, and carry heavy bags all by themselves. The seamless mobile app experience and rapid delivery cater to the modern demand for speed and efficiency.
Instant Gratification
Q-commerce fulfills immediate needs with delivery times in minutes rather than hours or days. This speed caters to impulse buys or last-minute essentials, enhancing the user experience. Such quick access ensures that consumers can promptly obtain what they need, minimizing disruption to their schedules.
Hyper-Localized Selection
With a focus on local stores and warehouses, Q-commerce offers items tailored to specific neighborhoods. This targeted selection allows customers to discover nearby products that are not available through traditional e-commerce. The local focus ensures the availability of fresh and relevant goods for single-person households or immediate needs.
Enhanced Market Reach
Q-commerce allows businesses to tap into new customer segments that prioritize speed and convenience over discounts. By offering ultra-fast delivery, companies can reach customers who may not have the time or inclination to visit physical stores. This expanded accessibility grows the potential customer base and overall revenue streams.
Optimized Inventory Management
Q-commerce leverages advanced analytics to manage inventory based on real-time demand and local trends. By strategically positioning micro-warehouses in high-demand areas, businesses minimize delivery times and enhance efficiency. This data-driven approach reduces waste and maximizes profits by ensuring the right products are always available.
Competitive Differentiation
Offering quick delivery distinguishes businesses from traditional e-commerce platforms, providing a competitive edge. This advantage can attract and retain customers who value speed and convenience, fostering loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
Quick commerce faces several operational hurdles that can impact profitability and sustainability.
Here's a breakdown of the key challenges,

“Customer loyalty in the Q-commerce space is unforgivingly low, making retention one of the biggest challenges for brands.”
"Sustainability remains a challenge in Q-commerce—companies must innovate to reduce carbon footprints while maintaining delivery speed."
As quick commerce continues to evolve, several innovative trends are poised to reshape its operations, enhance efficiency, and improve customer experiences.
Have a look at a few future trends of quick commerce,

Overview: Drones offer the potential to bypass traffic congestion and deliver products directly to customers' doorsteps, significantly reducing delivery times.
Impact: Implementing drone delivery can drastically cut down last-mile delivery costs and speed up the overall delivery process.
Challenges: Regulatory hurdles, safety concerns, and technological limitations currently hinder widespread adoption, but advancements are being made to address these issues.
Overview: Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in the quick commerce supply chain, improving inventory management and reducing fraud.
Impact: By providing a secure and immutable record of product origin, movement, and handling, blockchain can help ensure product quality and authenticity.
Benefits: This technology can streamline logistics, reduce administrative costs, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
Overview: AI and machine learning algorithms can optimize various aspects of quick commerce operations, from demand forecasting to route optimization.
Impact: Predictive analytics can help anticipate customer demand, allowing companies to stock the right products in the right locations.
Enhancements: AI-powered route optimization can minimize delivery times and fuel consumption, while chatbots can provide instant customer support.
Overview: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their purchases, leading quick commerce companies to adopt sustainable practices.
Initiatives: These include using electric vehicles for delivery, implementing eco-friendly packaging, and optimizing delivery routes to reduce carbon emissions.
Benefits: Sustainable practices not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Overview: Automating tasks within dark stores can increase efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Technologies: This includes using robots for picking and packing, automated storage and retrieval systems, and conveyor belts for order processing.
Impact: Automation can significantly speed up order fulfillment, reduce labor costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Overview: Quick commerce platforms are expanding beyond traditional categories like groceries and personal care items to include electronics, apparel, and other goods.
Customer Appeal: This expansion caters to a wider range of consumer needs and preferences, increasing the appeal of quick commerce services.
Challenges: It also requires careful management of inventory, logistics, and delivery processes to ensure a seamless customer experience.
Quick commerce marks a significant leap in retail evolution, addressing the modern consumer's need for speed and convenience.
Building upon the foundations of earlier e-commerce generations, Q-commerce prioritizes ultra-fast delivery by leveraging micro-warehouses and advanced logistics, shifting the focus from broad selection and discounts to localized availability and immediate fulfillment.
As this dynamic sector expands, partnering with a robust technology provider is crucial for success.
Fourchain, a leading mobile application development company,, offers advanced solutions designed to optimize your quick commerce operations, providing unparalleled visibility, streamlined processes, and efficient inventory management.
Discover how Fourchain can empower your business to thrive in the era of instant retail by contacting us today.
Want to build your own Q-commerce platform? Let’s talk!


Connect With Us Now
Drop us a line through the form below and we'll get back to you as soon as possible